Adding and Encoding information for XML Documents
he way that characters are represented by the underlying data stream is referred to as the encoding of a file. The specific encoding used is often present as the first few bytes in the file. An application checks these bytes upon opening the file and then knows how to display and manipulate the data.
There is also a default encoding if these first few bytes are not present. XML also has other ways of specifying how a file was encoded.
Unicode is a superset of every other significant computerized character set used in computer science today.
UTF-8 is the proper binary encoding of the Unicode character set. All XML documents should be generated exclusively in UTF-8 which will result in a more robust, more interoperable universe of documents.
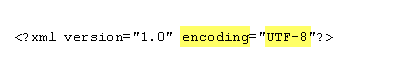


UTF stands for UCS (Universal Character Set) Transformation Format. UTF-8 represents a 7-bit character set or the characters 0 through 127.