| Lesson 3 | Attribute-list declaration syntax |
| Objective | Declare lists of attributes. |
Attribute-list Declaration Syntax
In the DTD, you declare lists of attributes in a manner similar to how you declare elements--by means of an attribute-list declaration.The MouseOver shows the generic syntax for declaring an attribute, an attribute-list declaration, and an example of attribute usage.
Note the composition of the ID value in the XML file as required by its type:
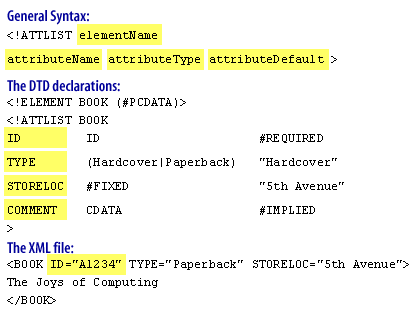
- The elementName represents the element for which the attribute (or attribute list) is being defined.
- The attributeName represents the name of the attribute being declared. Attribute names can contain letters, numbers, dashes, underscores, periods and colons.
- The attributeType specifies the kind of attribute this will be. There are eight types you can use when defining attributes; three are commonly used.
- The attributeDefault represents whether the attribute is required (#REQUIRED) or optional (#IMPLIED), and whether it has a fixed value (#FIXED value) or a specified default value from an enumerated list.
- The ID attribute had to be present and had to be of the ID type.
- The TYPE attribute was needed because the book would otherwise have been identified internally as having a "Hardcover" when in fact it was a "Paperback" type of book.
- The STORELOC attribute was optional, and this file would have been valid with or without this attribute/value pair. However, had any value other than "5th Avenue" been specified as the STORELOC attribute's value, this file would have been invalid.
- The COMMENT attribute was not required, and no comment was added to the BOOK element.
- The value for an ID type attribute cannot begin with a number. So while ID="1234" is not valid, ID= "A1234" is valid
Attribute Syntax Usage
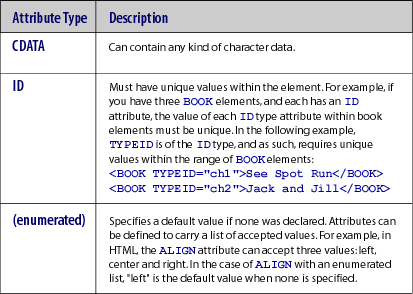
Attribute types
The table below contains the most commonly-used attribute types.
The next lesson defines the entities in a DTD.